What is GSM?
GSM, which stands for Global System for Mobile communications, reigns as the world’s most widely used cell phone technology. Cell phones use a cell phone service carrier’s GSM network by searching for cell phone towers in the nearby area.
The origins of GSM can be traced back to 1982 when the Groupe Spécial Mobile (GSM) was created by the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) for the purpose of designing a pan-European mobile technology.
It is approximated that 80 percent of the world uses GSM
 |
| GSM Architecture and Definitions |
Association (GSMA), which represents the interests of the worldwide mobile communications industry. This amounts to nearly 3 billion global people.
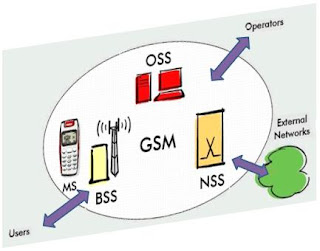
GSM Network Structure
The network is structured into a number of discrete sections:
* The Base Station Subsystem (the base stations and their controllers).
* The Network and Switching Subsystem (the part of the network most similar to a fixed network). This is sometimes also just called the core network.
* The GPRS Core Network (the optional part which allows packet based Internet connections).
* The Operations support system (OSS) for maintenance of the network.
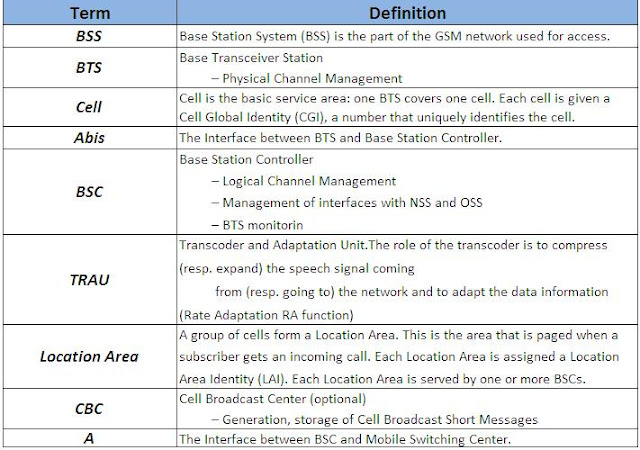
Now,We will explain the meaning of the GSM Network shortcuts.
PLMN: Public Land Mobile Network is area covered by one network operator. A PLMN can contain one or more MSCs.
GSM: Global System for Mobile communication
MS: Mobile Station is used by the subscriber for calling another subscriber either in the fixed network or in the mobile network.A Mobile Station (MS) is composed of a Mobile Termination (MT) and a Subscriber Module Identity (SIM) card.
MT: Mobile Termination.The MT performs the following functions:
- radio transmission termination;
- radio transmission channel management;
- terminal capabilities, including presentation of a man-machine interface to a user;
- speech encoding/decoding;
- error protection for all information sent across the radio path;
- flow control of signalling and user data;
- rate adaptation of user data between the radio channel rate and user rates;
- multiple terminal support;
- mobility management.
SIM: SIM card stores information concerning the subscriber such as subscriber identity,services subscribed, parameters for security procedures and information on the location of the subscriber (dynamically refreshed according to its movements).
Um > The Radio Interface between MS and Base Station.
UpLink: The Path of the Data from MS to Base Station.
DownLink: The Path of the Data from Base Station to MS.
 |
| GSM Architecture and Definitions |
 |
| GSM Architecture and Definitions |
Next
Refferance:
* Alcatel-Lucent
* Private Line
* Tutorials Point
* SS7 Training
