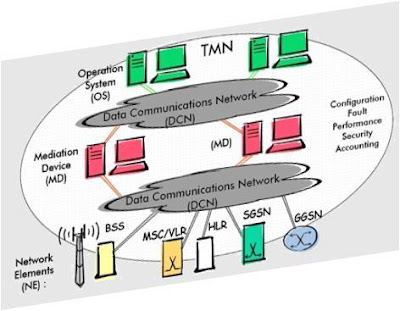
Cell-phone Codes
All cell phones have special codes associated with them. These codes are used to identify the phone, the phone's owner and the service provider.
Let's say you have a cell phone, you turn it on and someone tries to call you. Here is what happens to the call:
- When you first power up the phone, it listens for an SID (see sidebar) on the control channel. The control channel is a special frequency that the phone and base station use to talk to one another about things like call set-up and channel changing. If the phone cannot find any control channels to listen to, it knows it is out of range and displays a "no service" message.
- When it receives the SID, the phone compares it to the SID programmed into the phone. If the SIDs match, the phone knows that the cell it is communicating with is part of its home system.
- Along with the SID, the phone also transmits a registration request, and the MTSO keeps track of your phone's location in a database -- this way, the MTSO knows which cell you are in when it wants to ring your phone.
- The MTSO gets the call, and it tries to find you. It looks in its database to see which cell you are in.
- The MTSO picks a frequency pair that your phone will use in that cell to take the call.
- The MTSO communicates with your phone over the control channel to tell it which frequencies to use, and once your phone and the tower switch on those frequencies, the call is connected. Now, you are talking by two-way radio to a friend.
- As you move toward the edge of your cell, your cell's base station notes that your signal strength is diminishing. Meanwhile, the base station in the cell you are moving toward (which is listening and measuring signal strength on all frequencies, not just its own one-seventh) sees your phone's signal strength increasing. The two base stations coordinate with each other through the MTSO, and at some point, your phone gets a signal on a control channel telling it to change frequencies. This hand off switches your phone to the new cell.
 |
| Hand off switches your phone to the new cell |
Let's say you're on the phone and you move from one cell to another -- but the cell you move into is covered by another service provider, not yours. Instead of dropping the call, it'll actually be handed off to the other service provider.
If the SID on the control channel does not match the SID programmed into your phone, then the phone knows it is roaming. The MTSO of the cell that you are roaming in contacts the MTSO of your home system, which then checks its database to confirm that the SID of the phone you are using is valid. Your home system verifies your phone to the local MTSO, which then tracks your phone as you move through its cells. And the amazing thing is that all of this happens within seconds.
The less amazing thing is that you may be charged insane rates for your roaming call. On most phones, the word "roam" will come up on your phone's screen when you leave your provider's coverage area and enter another's. If not, you'd better study your coverage maps carefully -- more than one person has been unpleasantly surprised by the cost of roaming. Check your service contract carefully to find out how much you're paying when you roam.
Note that if you want to roam internationally, you'll need a phone that will work both at home and abroad. Different countries use different cellular access technologies. More on those technologies later. First, let's get some background on analog cell-phone technology so we can understand how the industry has developed.
Cell Phone Codes
Electronic Serial Number (ESN) - a unique 32-bit number programmed into the phone when it is manufactured
Mobile Identification Number (MIN) - a 10-digit number derived from your phone's number
System Identification Code (SID) - a unique 5-digit number that is assigned to each carrier by the FCC
While the ESN is considered a permanent part of the phone, both the MIN and SID codes are programmed into the phone when you purchase a service plan and have the phone activated.
"
Cell Phones (4)
" !